
EFFICACY & SAFETY
MONOFERRIC VS IRON SUCROSE
Hb INCREASES WERE NON-INFERIOR
WITH 1 DOSE OF MONOFERRIC VS UP
TO 5 DOSES OF IRON SUCROSE
FERWON-IDA
FERWON-NEPHRO
FERWON TRIALS:
FERWON-IDA
A randomized (2:1), open-label, non-inferiority, actively-controlled pivotal trial studying 1,512 adult patients with IDA and intolerance or lack of response to oral iron.1 Monoferric was intravenously administered as a single dose of 1000 mg. Iron sucrose was dosed at 200 mg per dose up to a maximum of 5 doses according to standard practice or physician choice. See full study design below.
Mean change in Hb levels from baseline (ITT Population) (co-primary endpoint)1,2
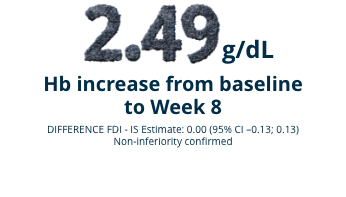

FERWON TRIALS:
FERWON-NEPHRO
A randomized (2:1), open-label, non-inferiority actively-controlled pivotal trial in 1,538 adult patients with IDA and chronic kidney disease (eGFR <60 mL/min).3 Monoferric was intravenously administered as a single dose of 1000 mg. Iron sucrose was dosed at 200 mg per dose up to a maximum of 5 doses according to standard practice or physician choice. See full study design below.
Mean change in Hb levels from baseline (ITT Population) (co-primary endpoint)2,3


KEY INSIGHTS FROM DR. HUZEFA BAHRAIN
Hear from Dr. Bahrain as he discusses why 1 dose of Monoferric is sufficient to replenish iron stores.

I’m Dr. Huzefa Bahrain, welcome to Monoferric Moments.
In my experience, we find that for most patients, just 1 dose of 1000 milligrams of Monoferric is sufficient to replenish iron stores.
Looking at all the intravenous iron infusions we’ve administered through clinical trials and commercial patients, Monoferric is observed as having a solid safety profile that is comparable to iron sucrose and is generally well tolerated by the vast majority of patients.
Monoferric has been evaluated in two clinical trials with a total of 3050 patients.
When looking at safety, there was no significant differences in adjudicated serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions between Monoferric and iron sucrose.
Only 0.3 percent of patients reported adjudicated serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions.
Monoferric was also evaluated in the PHOSPHARE study, which was two identical safety trials that were pooled to compare the incidence of hypophosphatemia with Monoferric vs ferric carboxymaltose.
Monoferric demonstrated significantly fewer incidences of hypophosphatemia than ferric carboxymaltose from baseline to day 35.
In the PHOSPHARE study, pooled results, only 8.0% of patients treated with Monoferric versus 74.4% of those treated with ferric carboxymaltose were noted to have hypophosphatemia.
For more information, explore Monoferric.com
HAVE QUESTIONS ABOUT THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF MONOFERRIC?
Sign up to contact a representative and receive information about Monoferric.
CONTACT US
FERWON-IDA
FERWON-NEPHRO
FERWON-IDA
- More patients achieved an Hb increase ≥2 g/dL at Week 1 (5.3% n=960 vs 2.5% n=477) and Week 2 (32.6% n=912 vs 20.8% n=452) with Monoferric compared to iron sucrose
- No significant differences were observed at Weeks 4 (56.9% n=903 vs 55.6% n=450) and 8 (67.1% n=903 vs 68.1% n=454)1
More patients achieved Hb increases ≥2 g/dL sooner with Monoferric vs iron sucrose1
(secondary endpoint)1
FERWON-NEPHRO
- More patients achieved an Hb increase of ≥1 g/dL at Week 1 (20.0% n=1002 vs 15.8% n=494) and Week 2 (34.6% n=980 vs 23.6% n=474) with Monoferric compared to iron sucrose
- No significant differences were observed at Week 8 (49.0% n=967 vs 47.6% n=475)3
More patients achieved Hb increases ≥1 g/dL sooner with Monoferric vs iron sucrose3
(secondary endpoint)3
CLINICAL TRIAL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adverse reactions were reported in 8.6% (172/2008) of patients treated with Monoferric vs. 9.0% (90/1000) of patients treated with IS2,4
- Adjudicated serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 0.3% (6/2008) of patients in the Monoferric group vs 0.2% (2/1000) of patients in the IS group2,4
- The incidence of hypophosphatemia is less than 4% for both the Monoferric and IS group2
Adverse reactions (≥1%) in patients receiving Monoferric in FERWON-IDA and FERWON-NEPHRO
(secondary endpoint)4
Hypophosphatemia (serum phosphate <2.0 mg/dL) was reported in 3.5% of Monoferric-treated patients in FERWON-IDA and FERWON-NEPHRO.
NO SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCES IN SERIOUS OR SEVERE HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS BETWEEN MONOFERRIC AND IRON SUCROSE
- Monoferric is contraindicated in patients with prior serious hypersensitivity reactions to Monoferric or any of its components4
- Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal, have been reported in patients receiving Monoferric.4 Patients may present with shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse
Incidence of serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions between Monoferric and iron sucrose
(co-primary endpoint)1,3
MONOFERRIC IMPROVED FACIT-FATIGUE SYMPTOM SCORES AT WEEK 8
- FACIT-fatigue symptom scores improved beyond severe fatigue starting at Week 1 (<30 FACIT-fatigue score)1
- In FERWON-IDA, there were no statistically significant differences between Monoferric and iron sucrose in increase in FACIT-fatigue score from baseline to Week 81
FERWON-IDA
Mean FACIT-fatigue symptom score* (secondary endpoint)1,2
*Score range from 0 to 52 with higher scores indicating less fatigue.
FERWON-IDA
Study Design
SEE STUDY +
CLOSE STUDY ^
FERWON-NEPHRO
Study Design
SEE STUDY +
CLOSE STUDY ^
These articles are provided by Pharmacosmos for discussion of FDA approved uses. Monoferric (ferric derisomaltose) should be used only according to the accompanying complete prescribing information.
SEE THE FULL
FERWON-IDA STUDY
READ FULL TEXT
SEE THE FULL
FERWON-NEPHRO STUDY
READ FULL TEXT
See Monoferric Full Prescribing Information
HAVE A QUESTION ABOUT MONOFERRIC?
Sign up to contact a representative and receive information about Monoferric.
LET US HELP
SEE MONOFERRIC VS FERRIC CARBOXYMALTOSE
Learn about the incidence of hypophosphatemia in the head-to-head PHOSPHARE trials.
REVIEW THE DATA
HOW MONOFERRIC WORKS
Monoferric has an innovative matrix structure that enables a slow and controlled release of bioavailable iron.
LEARN ABOUT IRON MATRIX STRUCTURE
INDICATIONS
Monoferric is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in adult patients:
- who have intolerance to oral iron or have had unsatisfactory response to oral iron
- who have non-hemodialysis dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD)
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Monoferric is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity to Monoferric or any of its components. Reactions have included shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal, have been reported in patients receiving Monoferric. Patients may present with shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Monoferric administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completion of the infusion. Only administer Monoferric when personnel and therapies are immediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions. Monoferric is contraindicated in patients with prior serious hypersensitivity reactions to Monoferric or any of its components. In clinical trials in patients with IDA and CKD, serious or severe hypersensitivity were reported in 0.3% (6/2008) of the Monoferric treated subjects. These included 3 events of hypersensitivity in 3 patients; 2 events of infusion-related reactions in 2 patients and 1 event of asthma in one patient.
Iron Overload
Excessive therapy with parenteral iron can lead to excess iron storage and possibly iatrogenic hemosiderosis or hemochromatosis. Monitor the hematologic response (hemoglobin and hematocrit) and iron parameters (serum ferritin and transferrin saturation) during parenteral iron therapy. Do not administer Monoferric to patients with iron overload.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions were reported in 8.6% (172/2008) of patients treated with Monoferric. Adverse reactions related to treatment and reported by ≥1% of the treated patients were nausea (1.2%) and rash (1%). Adjudicated serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 6/2008 (0.3%) patients in the Monoferric group. Hypophosphatemia (serum phosphate <2.0 mg/dL) was reported in 3.5% of Monoferric-treated patients in Trials 1 & 2.
To report adverse events, please contact Pharmacosmos at 1-888-828-0655. You may also contact the FDA at www.fda.gov/medwatch or 1-800-FDA-1088.
References:
- Auerbach M, Henry D, Derman RJ, Achebe MM, Thomsen LL, Glaspy J. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(9):1007‐1014.
- Data on File. 2021. Pharmacosmos Therapeutics Inc.
- Bhandari S, Kalra PA, Berkowitz M, Belo D, Thomsen LL, Wolf M. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021;36(1):111-120.
- Monoferric (ferric derisomaltose) Prescribing Information; Pharmacosmos Therapeutics Inc., Morristown, NJ: 2022.
- Wolf M, Rubin J, Achebe M, et al. JAMA. 2020;323(5):432‐443.